Vasco da Gama, The Portugese Navigator

 Explorer Vasco da Gama was born in Sines, Portugal, around 1460. In 1497, he was commissioned by the Portuguese king to find a maritime route to the East. His success in doing so proved to be one of the more instrumental moments in the history of navigation. He subsequently made two other voyages to India, and was appointed as Portuguese viceroy in India in 1524.
Explorer Vasco da Gama was born in Sines, Portugal, around 1460. In 1497, he was commissioned by the Portuguese king to find a maritime route to the East. His success in doing so proved to be one of the more instrumental moments in the history of navigation. He subsequently made two other voyages to India, and was appointed as Portuguese viceroy in India in 1524.
Early Years
Vasco da Gama was born into a noble family around 1460 in Sines, Portugal. Little is known about his upbringing except that he was the third son of Estêvão da Gama, who was commander of the fortress in Sines in the southwestern pocket of Portugal. When he was old enough, young Vasco da Gama joined the navy, where was taught how to navigate.
 Known as a tough and fearless navigator, da Gama solidified his reputation as a reputable sailor when, in 1492, King John II of Portugal dispatched him to the south of Lisbon and then to the Algarve region of the country, to seize French ships as an act of vengeance against the French government for disrupting Portuguese shipping.
Known as a tough and fearless navigator, da Gama solidified his reputation as a reputable sailor when, in 1492, King John II of Portugal dispatched him to the south of Lisbon and then to the Algarve region of the country, to seize French ships as an act of vengeance against the French government for disrupting Portuguese shipping.
Following da Gama’s completion of King John II’s orders, in 1495, King Manuel took the throne, and the country revived its earlier mission to find a direct trade route to India. By this time, Portugal had established itself as one of the most powerful maritime countries in Europe.
Much of that was due to Henry the Navigator, who, at his base in the southern region of the country, had brought together a team of knowledgeable mapmakers, geographers and navigators. He dispatched ships to explore the western coast of Africa to expand Portugal’s trade influence. He also believed that he could find and form an alliance with Prester John, who ruled over a Christian empire somewhere in Africa. Henry the Navigator never did locate Prester John, but his impact on Portuguese trade along Africa’s east coast during his 40 years of explorative work was undeniable. Still, for all his work, the southern portion of Africa—what lay east—remained shrouded in mystery.
In 1487, an important breakthrough was made when Bartolomeu Dias discovered the southern tip of Africa and rounded the Cape of Good Hope. This journey was significant; it proved, for the first time, that the Atlantic and Indian oceans were connected. The trip, in turn, sparked a renewed interest in seeking out a trade route to India.
By the late 1490s, however, King Manuel wasn’t just thinking about commercial opportunities as he set his sights on the East. In fact, his impetus for finding a route was driven less by a desire to secure for more lucrative trading grounds for his country, and more by a quest to conquer Islam and establish himself as the king of Jerusalem.
First Voyage
Historians know little about why exactly da Gama, still an inexperienced explorer, was chosen to lead the expedition to India in 1497. On July 8 of that year, he captained a team of four vessels, including his flagship, the 200-ton St. Gabriel, to find a sailing route to India and the East.
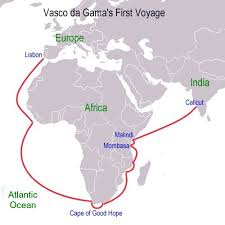 To embark on the journey, da Gama pointed his ships south, taking advantage of the prevailing winds along the coast of Africa. His choice of direction was also a bit of a rebuke to Christopher Columbus, who had believed he’d found a route to India by sailing east.
To embark on the journey, da Gama pointed his ships south, taking advantage of the prevailing winds along the coast of Africa. His choice of direction was also a bit of a rebuke to Christopher Columbus, who had believed he’d found a route to India by sailing east.
Following several months of sailing, he rounded the Cape of Good Hope and began making his way up the eastern coast of Africa, toward the uncharted waters of the Indian Ocean. By January, as the fleet neared what is now Mozambique, many of da Gama’s crew members were sick with scurvy, forcing the expedition to anchor for rest and repairs for nearly one month.
In early March of 1498, da Gama and his crew dropped their anchors in the port of Mozambique, a Muslim city-state that sat on the outskirts of the east coast of Africa and was dominated by Muslim traders. Here, da Gama was turned back by the ruling sultan, who felt offended by the explorer’s modest gifts.
By early April, the fleet reached what is now Kenya, before setting sail on a 23-day run that would take them across the Indian Ocean. They reached Calicut, India, on May 20. But da Gama’s own ignorance of the region, as well as his presumption that the residents were Christians, led to some confusion. The residents of Calicut were actually Hindu, a fact that was lost on da Gama and his crew, as they had not heard of the religion.
Still, the local Hindu ruler welcomed da Gama and his men, at first, and the crew ended up staying in Calicut for three months. Not everyone embraced their presence, especially Muslim traders who clearly had no intention of giving up their trading grounds to Christian visitors. Eventually, da Gama and his crew were forced to barter on the waterfront in order to secure enough goods for the passage home. In August of 1498, da Gama and his men took to the seas again, beginning their journey back to Portugal.
Da Gama’s timing could not have been worse; his departure coincided with the start of a monsoon. By early 1499, several crew members had died of scurvy and in an effort to economise his fleet, da Gama ordered one of his ships to be burned. The first ship in the fleet didn’t reach Portugal until July 10, nearly a full year after they’d left India.
In all, da Gama’s first journey covered nearly 24,000 miles in close to two years, and only 54 of the crew’s original 170 members survived.
Second Voyage
When da Gama returned to Lisbon, he was greeted as a hero. In an effort to secure the trade route with India and usurp Muslim traders, Portugal dispatched another team of vessels, headed by Pedro Álvares Cabral. The crew reached India in just six months, and the voyage included a firefight with Muslim merchants, where Cabral’s crew killed 600 men on Muslim cargo vessels. More important for his home country, Cabral established the first Portuguese trading post in India.
 In 1502, Vasco da Gama helmed another journey to India that included 20 ships. Ten of the ships were directly under his command, with his uncle and nephew helming the others. In the wake of Cabral’s success and battles, the king charged da Gama to further secure Portugal’s dominance in the region.
In 1502, Vasco da Gama helmed another journey to India that included 20 ships. Ten of the ships were directly under his command, with his uncle and nephew helming the others. In the wake of Cabral’s success and battles, the king charged da Gama to further secure Portugal’s dominance in the region.
To do so, da Gama embarked on one of the most gruesome massacres of the exploration age. He and his crew terrorised Muslim ports up and down the African east coast, and at one point, set ablaze a Muslim ship returning from Mecca, killing the several hundreds of people (including women and children) who were on board. Next, the crew moved to Calicut, where they wrecked the city’s trade port and killed 38 hostages. From there, they moved to the city of Cochin, a city south of Calicut, where da Gama formed an alliance with the local ruler.
Finally, on February 20, 1503, da Gama and his crew began to make their way home. They reached Portugal on October 11 of that  year.
year.
Later Years
Little was recorded about da Gama’s return home and the reception that followed, though it has been speculated that the explorer felt miffed at the recognition and compensation for his exploits.
Married at this time, and the father of six sons, da Gama settled into retirement and family life. He maintained contact with King Manuel, advising him on Indian matters, and was named count of Vidigueira in 1519. Late in life, after the death of King Manuel, da Gama was asked to return to India, in an effort to contend with the growing corruption from Portuguese officials in the country. In 1524, King John III named da Gama Portuguese viceroy in India.
That same year, da Gama died in Cochin—the result, it has been speculated, from possibly overworking himself. His body was sailed back to Portugal, and buried there, in 1538.

